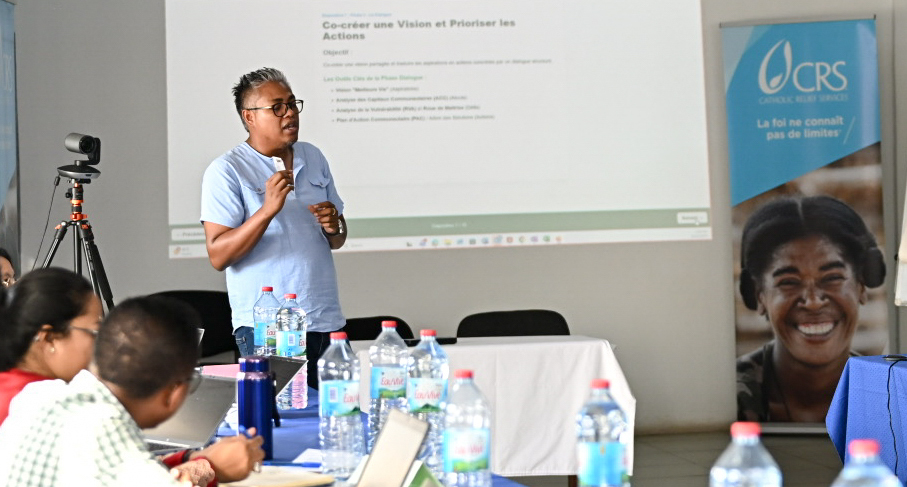
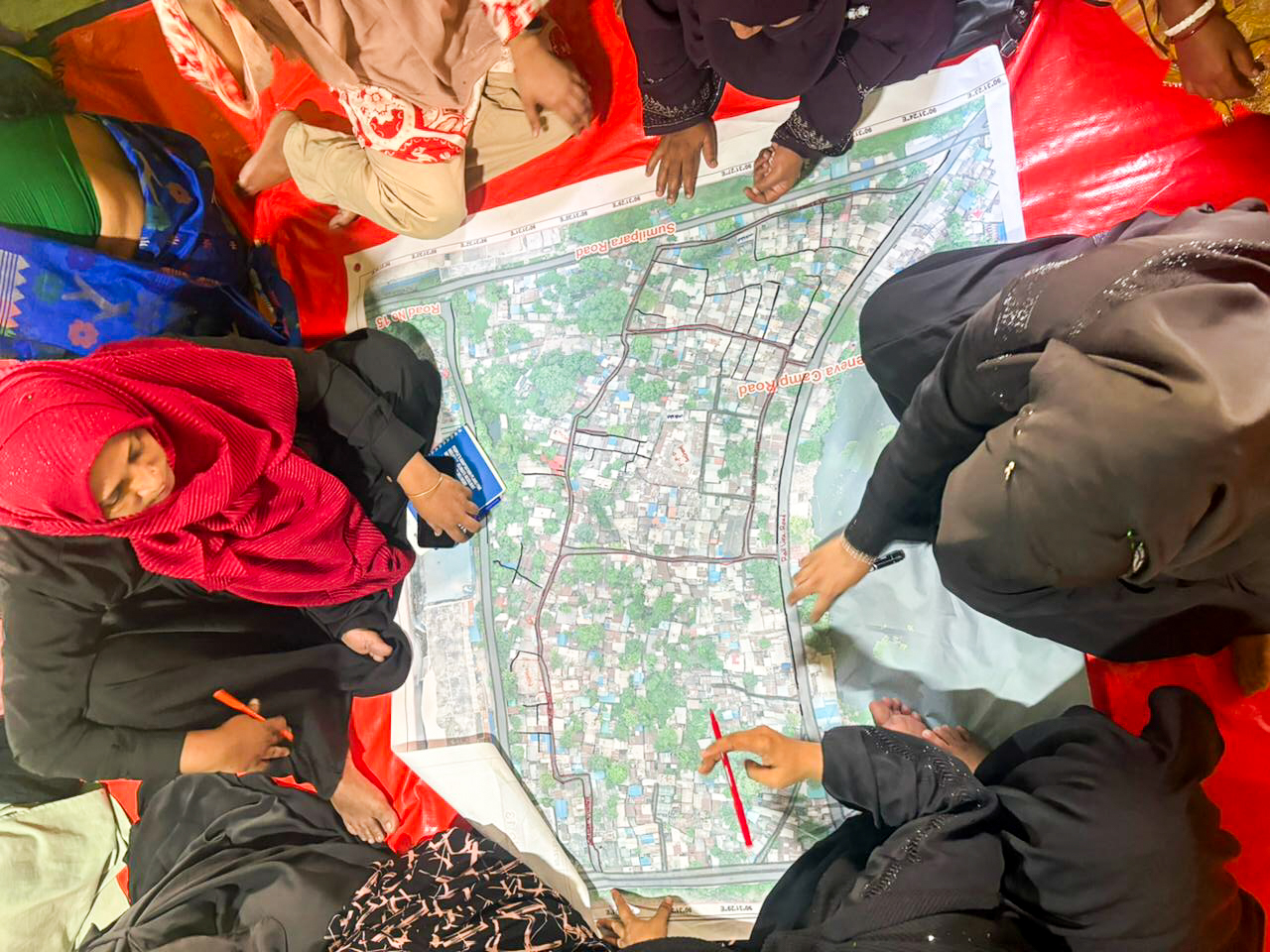
Southern Madagascar faces severe climate vulnerability, with recurrent droughts, low rainfall, and chronic food insecurity deepening poverty. The World Bank’s MIONJO Project (launched 2020) aims to strengthen basic services, local governance, and climate resilience. GCA, with the Government of Madagascar, the World Bank and CRS, is embedding Locally Led Adaptation by developing a People’s Adaptation Planning process in three communes. The approach enables communities to identify climate risks and shape resilience investments. The People's Adaptation Planning process is being integrated into national planning systems (including the PDLII), building institutional capacity and supporting replication across the country.





-(1).jpg)











.jpg)
-action---displaced-communities-and-the-search-for-durable-solutions-1.jpg)








-(1).jpg)












.jpg)
-action---displaced-communities-and-the-search-for-durable-solutions-1.jpg)




